Quality Management
Essential Idea: Quality management focuses on producing products of consistent required quality.
Quality control (QC) [process]
Quality control: Tolerances (an acceptable amount of defect) are defined at the design stage of the product. Parts not within tolerance need to be reworked or scrapped. Continuous monitoring ensures that machines perform to the predetermined standard/quality.
Quality control at the source eliminates waste from defects as the workers are responsible for the quality of work they do.
Statistical process control (SPC)
This is a quality control tool that uses statistical methods to ensure that a process operates at its most efficient. This is achieved through measuring aspects of a component to ensure that it meets the required standard throughout its production in order to eliminate waste.

Real time SPC contributes and assists with:
- Reducing costs
- Improving productivity
- Decision making in real time
- Reducing waste
- Reducing variability in outcome
- Discovering abnormalities
- Speeding up process changes
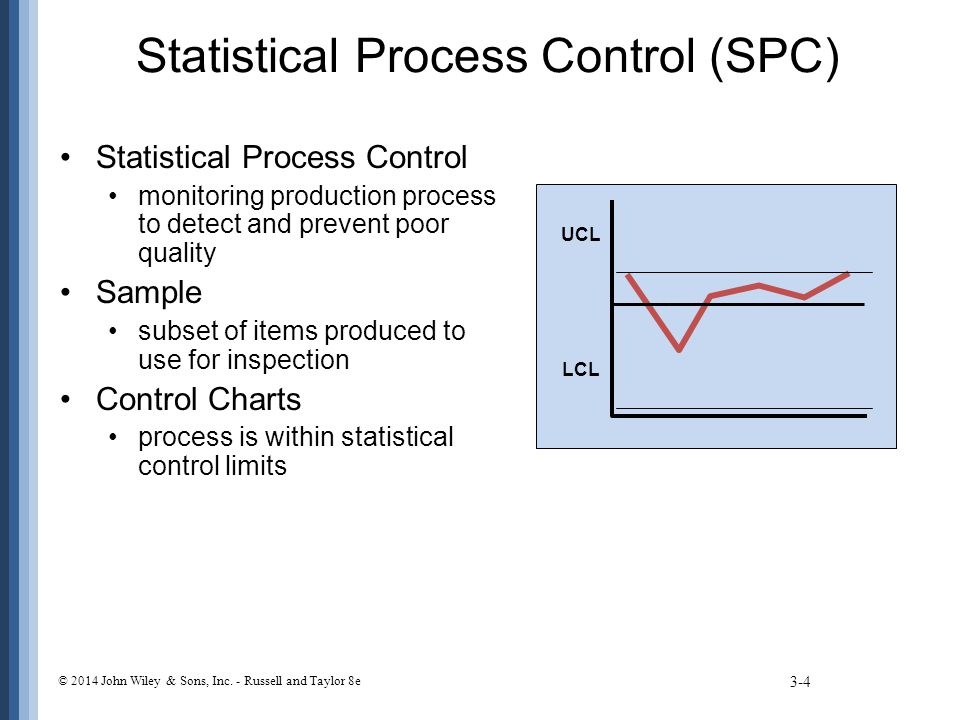
Statistical Process Control Charts:
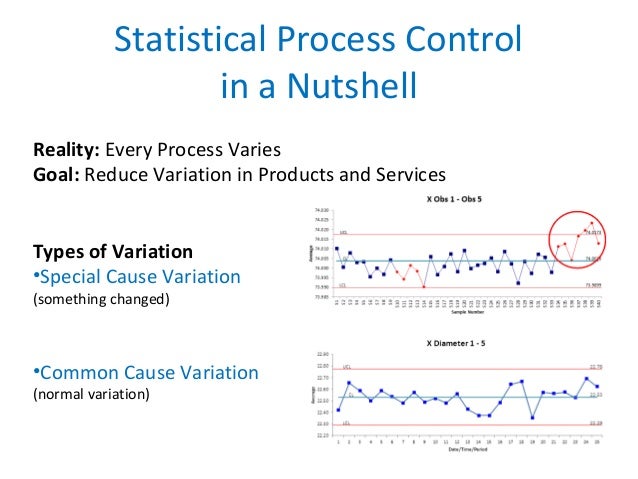
Quality assurance (QA) [product]
This covers all activities from design to documentation. It also includes the regulation of the quality of raw materials, assemblies, products and components, services related to production, and management and inspection processes.
Quality assurance is a way of preventing mistakes or defects in manufactured products and avoiding problems when delivering solutions or services to customers. Defect prevention in quality assurance differs subtly from defect detection and rejection in quality control, and has been referred to as a shift left as it focuses on quality earlier in the process.
| Quality Assurance Framework |
The Differences between QA, QC and SPC
QA is process oriented while QC is product oriented. QA deals in developing processes and systems that align with Quality Management. QC on the other hand deals with monitoring products.
For example, a QA engineer would develop a quality plan based on customer requirements and a QC engineer would monitor and ensure that all requirements of the quality plan are met during manufacturing. The QC engineer would only focus on making sure the product meets the requirements of the quality plan as set by the QA.
QA is the part of QM focused on providing confidence that quality requirements will be fulfilled.
QC is the part of QM focused on fulfilling quality requirements.
 |
| Differences between QC and QA |

No comments:
Post a Comment