Invention
Essential Idea: The protection of a novel idea of how to solve a problem is a major factor in commercial design.
Invention is the process of discovering a principle which allows a technical advance in a particular field that results in a novel/new product. Often, inventions solve problems of the real world.
Drivers for Invention
Drivers for invention include personal motivation to express creativity or for personal interest, scientific or technical curiosity, constructive discontent, the desire to make money, or the desire to help others.
Expression of creativity / Personal interest
The inventor might have a personal motivation to invent - it could be out of personal interest (a tinkerer) or creative expression.
Constructive discontent
The inventor is not happy with an existing product, and aims to make it better.
Scientific or technical curiosity
Some inventors are just simply curious which leads them to invent new revolutionary items that require inquisitive scientific or technical thinking.
Desire to make money
For products and systems to develop, ie. further iterations, to evolve then the financial return will fund the research and development work to enable the designer to increase the amount of new inventions and innovations.
Desire to help others
Some inventions are made to assist people and make life better; an example would be Illac Diaz and how he used a solar light made from old soda bottles to bring natural light into the homes of some of the poorest people in the Philippines.

The Lone Inventor
An individual working outside or inside an organization who is committed to the invention of a novel product and often becomes isolated.
The advantages and disadvantages of being a lone inventor;
An individual working outside or inside an organization who is committed to the invention of an original or novel product often becomes isolated because he/she is engrossed with ideas that imply change and are resisted by others. Designers/Engineers/Inventors such as James Dyson, Trevor Bayliss and Clive Sinclair fit this description of a 'lone inventor'. Nowadays, most products are made by teams of designers whom of which bring their own expertise and specialties to the table (multidisciplinary teams)
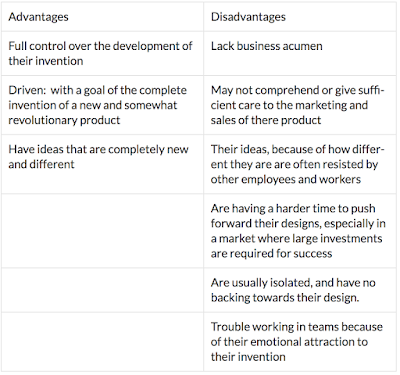 |
| advantages and disadvantages |
Intellectual Property (IP)
Intellectual property is a legal term used for intangible property such as creations of the mind, such as signs an inventions used in a commercial setting. Intellectual property is also protected by the law [legally recognized], and includes protection of inventions, designs, art, music, literature, etc.
- Owners are granted certain exclusive rights to a variety of intangible asssets such as musical, literary, and artistic works, discoveries and inventions, and words, phrases, sumbols, and designs.
- Common types of intellectual property rights include;
- Copyright
- Trademarks
- Patents
- Industrial Design Rights
- Trade Dress
- in some jurisdictions, Trade Secrets
- Why do people use intellectual property rights?
- Differentiating from competitors
- Selling or licensing to provide revenue streams
- Offering customers something new and different
- Marketing and branding
- Value as an asset
Strategies for Protecting IP: Patents, Trademarks, Design protection, Copyright.
Patent pending
| Products are protected using patent pending. |
Trademark
 |
| Company trademarks are recognizable by its design. |
Copyright

Copyright is a legal right created by the law of a country that grants the creator of an original work exclusive rights to its use and distribution, usually for a limited time, with the intention of enabling the creator to receive compensation for their intellectual effort.
Registered trademark
The essential function of a trademark is to exclusively identify the commercial source or origin of products or services. A trademark indicates a source or serves as a badge of origin.
Service mark
Shelved Technologies
Reasons why some patented technologies are shelved
Cost effectiveness
The technology is available, but the cost of using it in products makes it too expensive for the consumer, eg. 3D printers for home use - although this is changing now.
Social
Market is not ready for the change. For example, the football goal line technology (putting a chip in the football to see if it passed the goal line or not) but there is a lot of resistance to this technology; people don't want to technologize aspects of football.
Technological
The science and underpinning ideas have been developed, but technology is not resolved enough to introduce the product, for example, flexible phones.




