Thermoplastics are liner chain molecules, sometimes with side bonding of the molecules but with weak secondary bonds between the chains. Between the long chain molecules are secondary bonds which are weak forces of attraction between the molecules.
Thermoplastics can be heated and reformed. They can be reused (in comparison to thermosetting plastics).
| Thermoplastic polymer structure |
 |
| Production of thermoplastics |
- Ductile
- Low stiffness -squishy water bottles for example
- Easily injected into a mold
- Can be reshaped after heating
- Easily and cost effectively manufactured
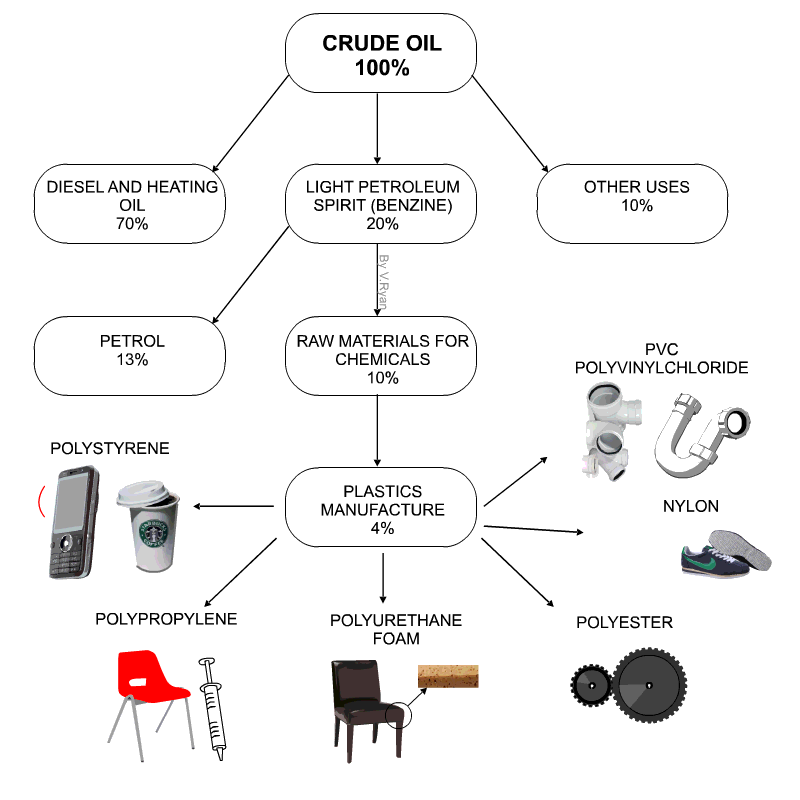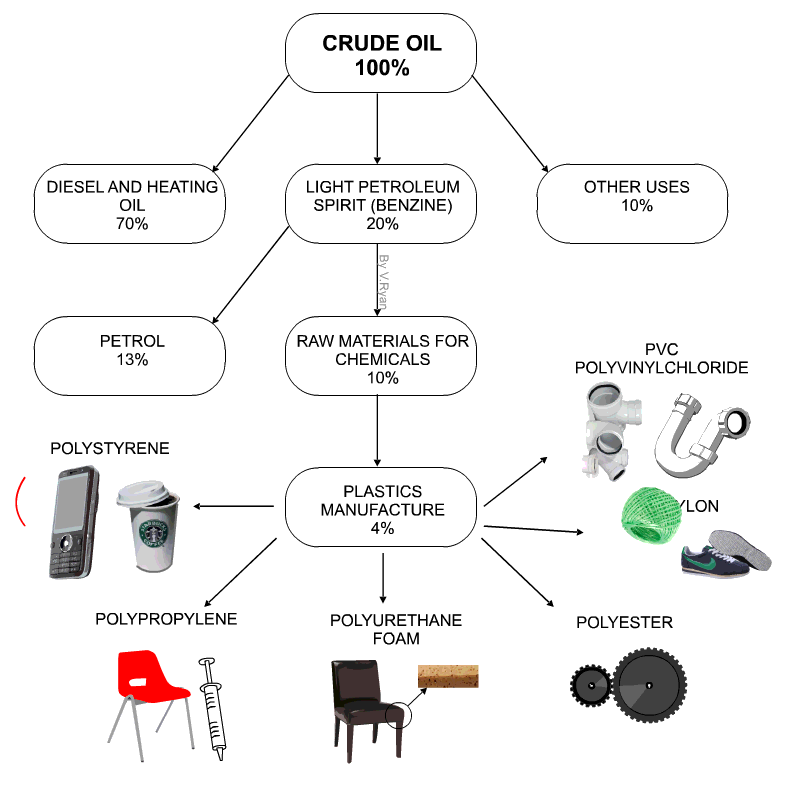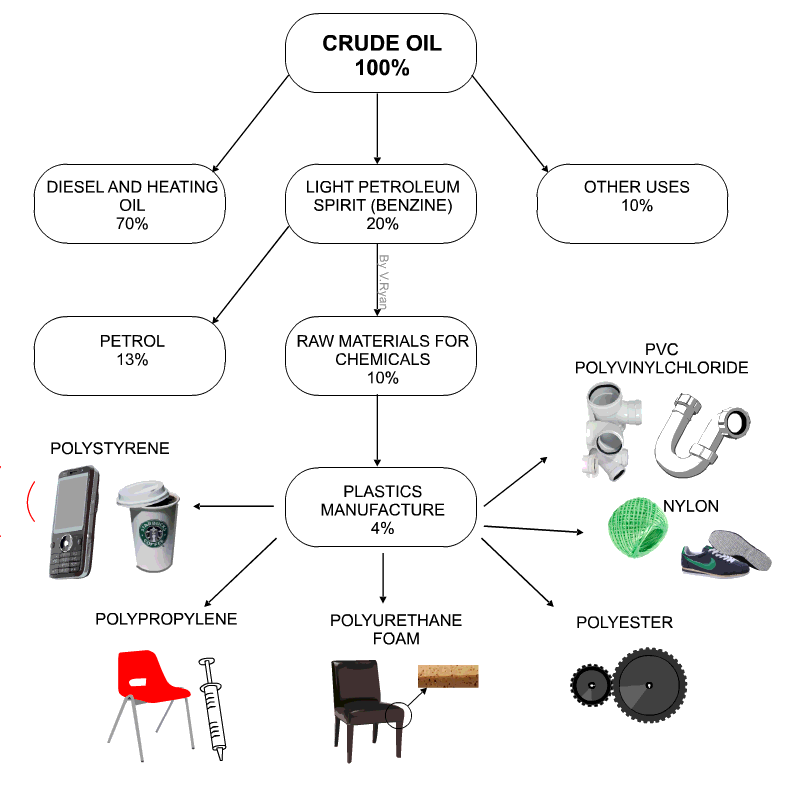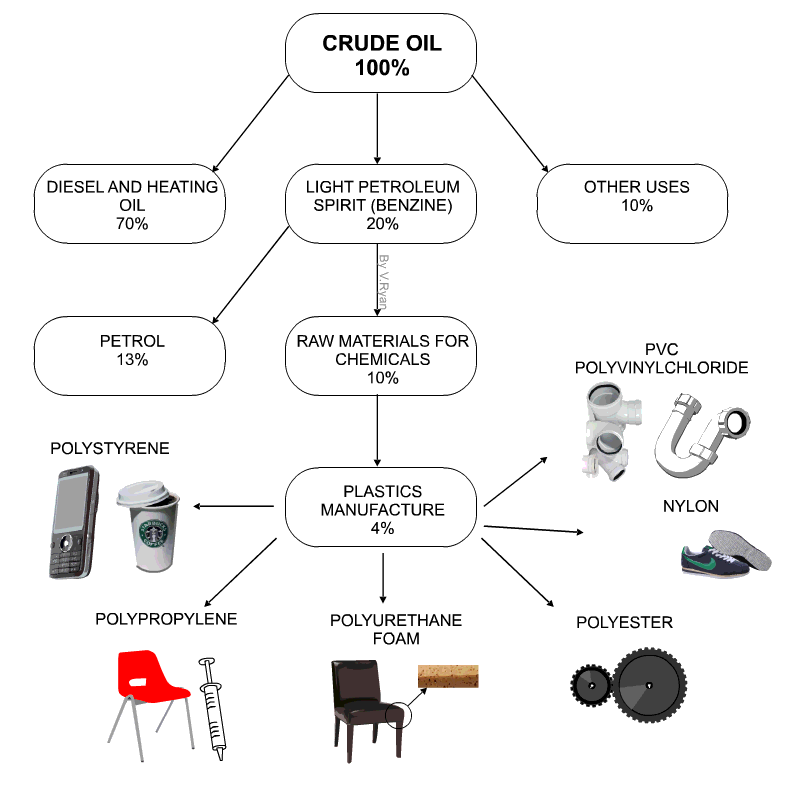
Uses of thermoplastics:
Thermosets are linear chain molecules but with strong primary bonds between adjacent polymer chains (or cross links). This gives thermosets a rigid 3d structure.
Thermosetting plastics can only be reformed once - the shape is permanently set and is permanently locked.
| Thermosetting plastic polymer structure |
 |
| Production of thermosetting plastics |
- Higher stiffness
- Higher strength than thermoplastics
- Cannot be reheated and remoulded - it will usually char
Uses of thermosetting plastics:
Nearly all types of plastics can be recycled, however the extent to which they are recycled depends upon technical, economic, and logistic factors. as a valuable and finite resource, the optimum recovery route for most plastic items at the 'end-of-life- is to be recycled, preferably back into a product that can then be recycled again and again and so on.
- Thermoplastics can be easily recycled
- Thermoplastics come in a range of chemical compounds and therefore need to be sorted for recycling
- Thermosets are not so easy (and expensive to do so).
- Often get sent to the landfill
Example - Plastics can be recycled into clothes (recycled polyester)
BENEFITS OF RECYCLING:
BENEFITS OF RECYCLING:
- sustainable source of raw materials
- reduces environmental impact of plastic-rich products
- minimizes the amount of plastic being sent to the landfill sites
- avoids the consumption of the Earth's oil stocks
- consumes less energy than producing new, virgin polymers
- encourages a sustainable lifestyle among children and young adults
Bioplastics
To reduce the problems of disposing of plastics they can be designed to be biodegradable, known as bioplastics. These are plastics derived from renewable sources, such as vegetable fats and oil, corn starch, pea starch or microbiota.
Production of oil based plastics tend to require more fossil fuels and to produce more greenhouse gasses than the production of bio-based polymers.
Some, but not all, bioplastics are designed to biodegrade.
| Process of bioplastic production |
Helpful links:
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/design/resistantmaterials/materialsmaterialsrev3.shtml
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/design/resistantmaterials/materialsmaterialsrev3.shtml