Beyond Usability: Designing for pleasure and emotion
Usability is not the only factor for a designer to consider; products can be designed to evoke pleasure and emotion.
FOUR-PLEASURE FRAMEWORK:
- Socio-pleasure:
- Socio-pleasure can be derived from social interaction and are concerned with pleasures derived from social signifiers of belonging, social-enablers and other social self-identification factors.
- Examples include email, internet, and mobile phones that facilitate communication between people.
- Physio-pleasure:
- Is derived from the feel of a product during use from a human's senses, such as the smell, taste, feel of the object.
- Examples include: wearing a silk garment, taste of a food, smell of leather, a new car, coffee, or freshly baked bread
 |
| The new car smell is an example of physio-pleasure |
- Psycho-pleasure:
- Is derived from the cogonanitive demands of using a product or service and the emotional reactions engendered through the experience of using it
- Examples include: products that were improved or redesigned from the previous type
 |
| The Behmor coffee maker is advanced and convenient |
- Ideo-pleasure
- Ideo-pleasures are pleasures that are linked to our ideals, aesthetically, culturally, and otherwise to satisfy people's tastes, values and aspirations.
- Examples include a product made from biodegradable materials that might be perceived as embodying the value of environmental responsibility.
| Organic products embodies healthy food |
Design for emotion:
- Visceral design: Design that speaks to people's nature in terms of how the expect products and systems to function and how they expect to interact with them
- Reflective Design: Design that evokes personal memory focussing on the message, culture and meaning or the use of the product
- Behavioural design: Focussed on use and understanding, this considers how people will use a product, focussing on functionality

- https://usabilla.com/blog/designing-usability-just-isnt-enough/
The attract-converse-transact (ACT) model
The ACT model is a framework for creating designs that improve the relations of users with a product and intentionally trigger emotional responses.
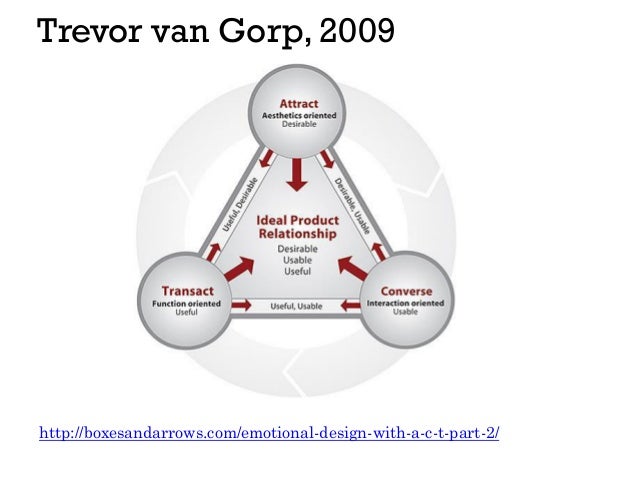

- The attract part of the model is aesthetics oriented
- The converse part of the model is interaction oriented
- The transact part of the model is function oriented


No comments:
Post a Comment