Manufacturing Processes
Essential idea: Different manufacturing processes have been developed to innovate existing products and create new products.
Designers sometimes engineer products in such a way that they are easy to manufacture. Design for manufacture (DfM) exists in almost all engineering disciplines, but differs greatly depending on the manufacturing technologies used. This practice not only focuses on the design of a product's components, but also on quality control and assurance.
Additive Techniques
Paper-based rapid prototyping
PRP technology at the moment only used for for prototyping purposes and does not offer the same design freedom and strength as for example, a Selective Laser Sintered (SLS).
Laminated object manufacture (LOM)
LOM is used to make 3D paper/thin polymer models and is a form of 3D printing. It is often used for creating scale models and conceptual prototypes that can be tested for form or design. It can also be used to make patterns for use in traditional manufacturing, such as sand molded casting.
- Materials include paper, plastic or metal
- Design contexts include models, prototypes, vacuum forming molds, pattern (for casting), or one-off products.
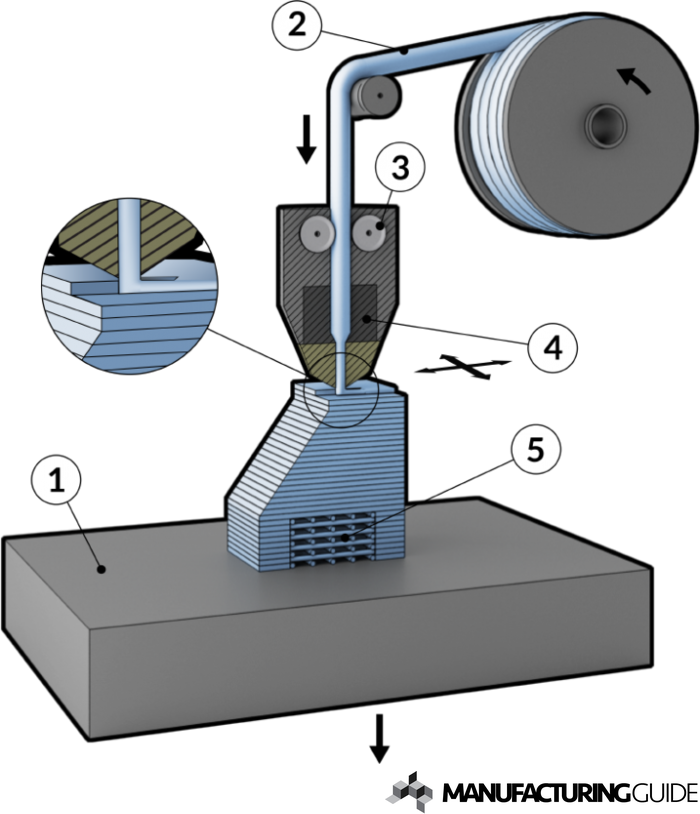
3D Printing and Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM)
Fused Deposition Modelling process constructs three-dimensional objects directly from 3D CAD drawings. A temperature controlled head extrudes thermoplastic material layer by layer.
- Importing an STL file of a modelled into horizontal layers , which is then sliced into horizontal layers
- The material used for objects 3D printed by an FDM would generally be PLA - less harmful to the environment, as it is made out of cornstarch. ABS is not as good for the environment because it is synthetically made.
The result of the solidified material laminating into the preceding layer is a plastic 3D model built up one strand at a time.
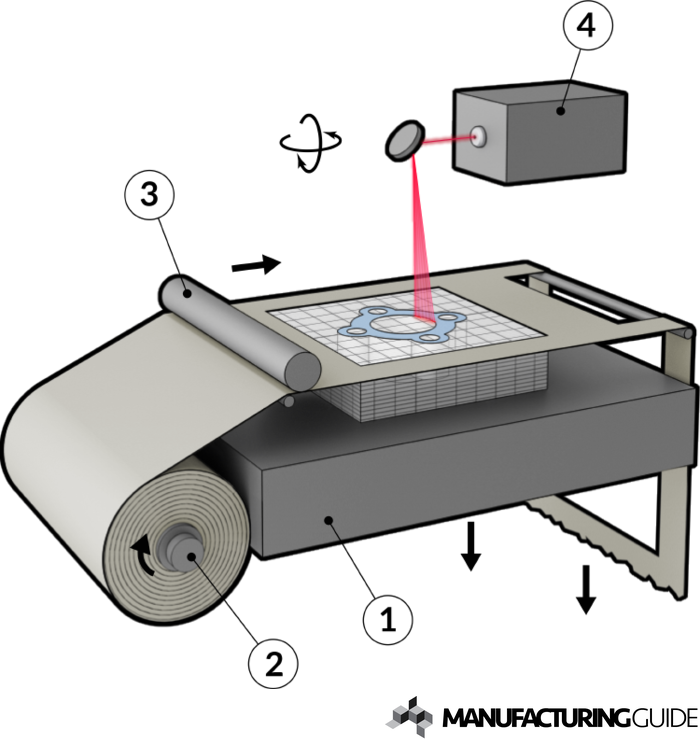
Stereolithography (SLA)
Stereolithography is an additive manufacturing technology that builds objects one layer at a time by curing a photo-reactive resin with a UV laser or other similar power source.
- Type of liquid or polymer that reacts and hardens to the laser beam
- Liquid material is hardened on contact
- Laser builds from the bottom up


Wasting/Subtractive Techniques
Manufacturing techniques that cut away material in order to create a component.
Cutting
Cutting describes the action sawing, chiseling, and planing which removes material in the process of cutting.
| Band Saw |
Advantages
- equipment and CNC have a high accuracy
- equipment and CNC produce a high quality finish
- produce very fine details
- minimal distortion
Disadvantages
- equipment and CNC initial costs are high
- special training/skills are required
Powered machines that shape materials through a variety of cutting processes, machine tools operate on unfinished metal parts, such as rough metal castings or forgings, and perform shaping and finishing operations that produce precisely dimensioned parts. Most machine tools function in one or more several basic categories - drilling, turning, and milling.
.jpg) |
| Drill Press |
| Mill machine |
Advantages
- High accuracy can be achieved
- equipment and CNC produce a high quality finish
- produce very fine details
- CNC/CAM allows for 24/7 production
Disadvantages
- equipment and CNC initial costs are high
- special training/skills are required
- less workers requires in a CNC/CAM work environment
Turning is most commonly carried out using a lathe or milling machine. Lathes are mostly used for cutting metals or woods. They work on a horizontal axes where the workpiece rotates at speed and tools such as chisels remove waste materials.
Abrading
Abrading involves the use of abrasive materials to wear away the material by friction. This can be done using abrasive papers (eg. sandpaper) or emery cloth. It could also involve the process of grinding use a wheel or abrasive stone. Synthetic materials such as silicon carbide, aluminum oxide or industrial diamond tipped tools can be used. As with cutting the tool must be harder than the material being cut or abraded.

Advantages
- provides a good finish
- takes sharp edges away – safety
- Cheap shaping technique – relatively low capital cost
- can be noisy so health hazard
- can be dusty so health hazard
Moulding
Thermoforming
Laminating
Casting
Knitting
Weaving
Permanent Joining Techniques
Fastening
Adhering
Fusing
Temporary Joining Techniques








No comments:
Post a Comment