Graphical Modelling
Essential Idea: Graphical models are used to communicate design ideas
Graphical models can take many forms, but their
prime function is always the same—to simplify the
data and present it in such a way that understanding
of what is being presented aids further development
or discussion.
Designers utilize graphical modelling
as a tool to explore creative solutions and refine ideas from the technically impossible to the technically possible, widening the constraints of what is feasible.
2D and 3D graphical models
2D physical models: Using sheet materials such as card or polypropylene can be used to make 2d physical models. 2D physical modelling is an extension of sketching and provides the designers with some solutions to their thinking and enables them to progress with their idea knowing that their ideas function.
2D Virtual Modelling: can also be hand drawn
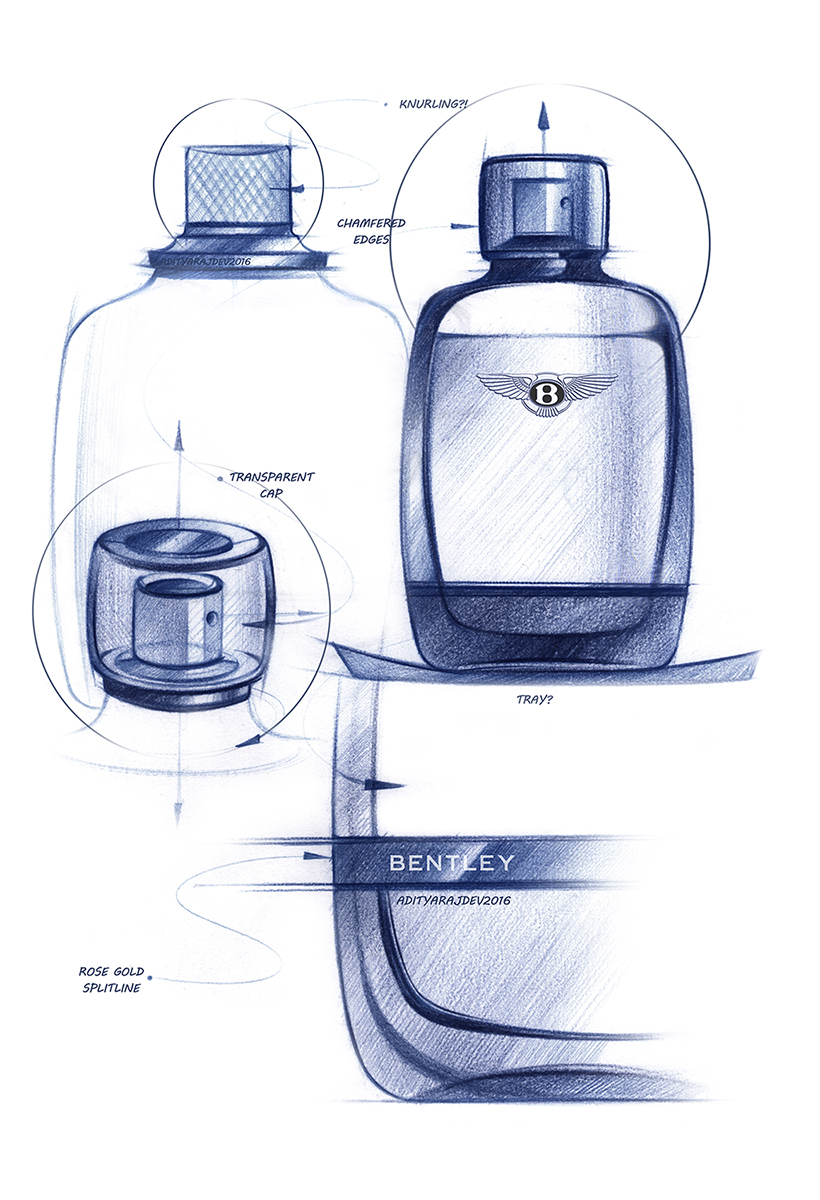
3D Models: Designers use models as a representation of reality and as a representation of the selected features of a design. Models can be used throughout the design process from conceptual thinking to final development. Can be done in two ways – physical modelling and virtual modelling

Perspective and scale drawings
Projection Drawings Systems of drawings that are accurately drawn, the two main types are isometric projection (formal drawing technique) or orthographic projection (working drawing technique)
Scale Drawings Drawings that are bigger or smaller than the real product, but exactly in proportion with product
Working Drawings Drawings that are used to guide the production of a product, most commonly orthographical projection, section drawings, part drawings, assembly drawings and plan drawings.
Orthographic Drawings / Orthogonal / Projections
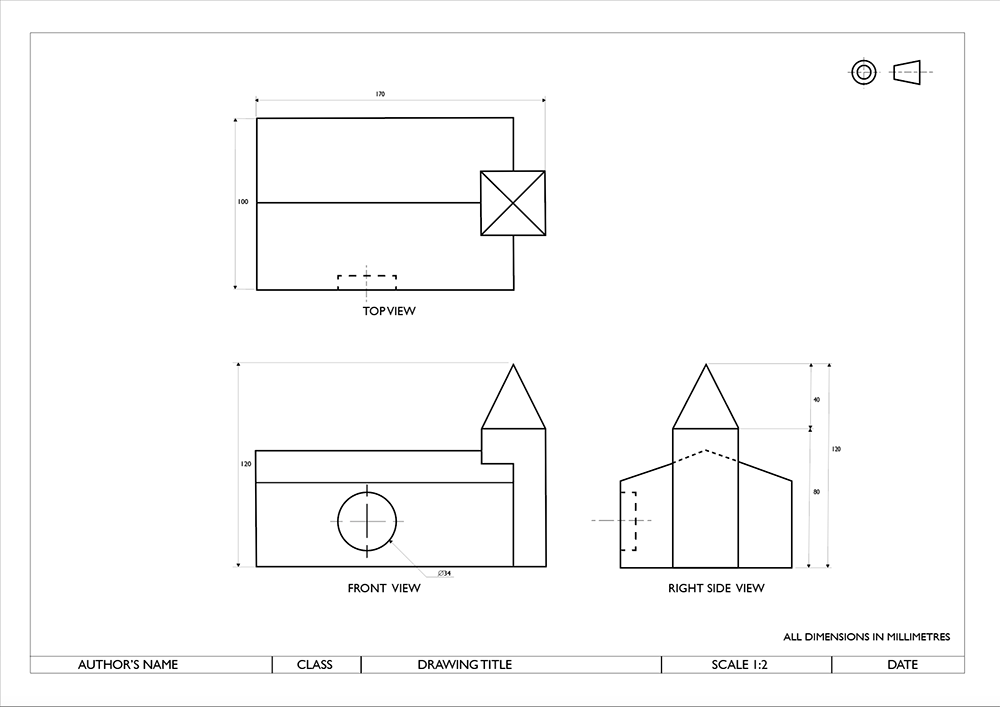
- A series of flat (2D) views of an object showing it exactly as it is in shape and size i.e. constructional details.
- An orthographic drawing shows all details and dimensions and is usually used as a production/working drawing.
- It is a convergent thinking style of drawing.
- Orthographic drawings are produced at the final solution stage and are used as working drawings in the realization stage.
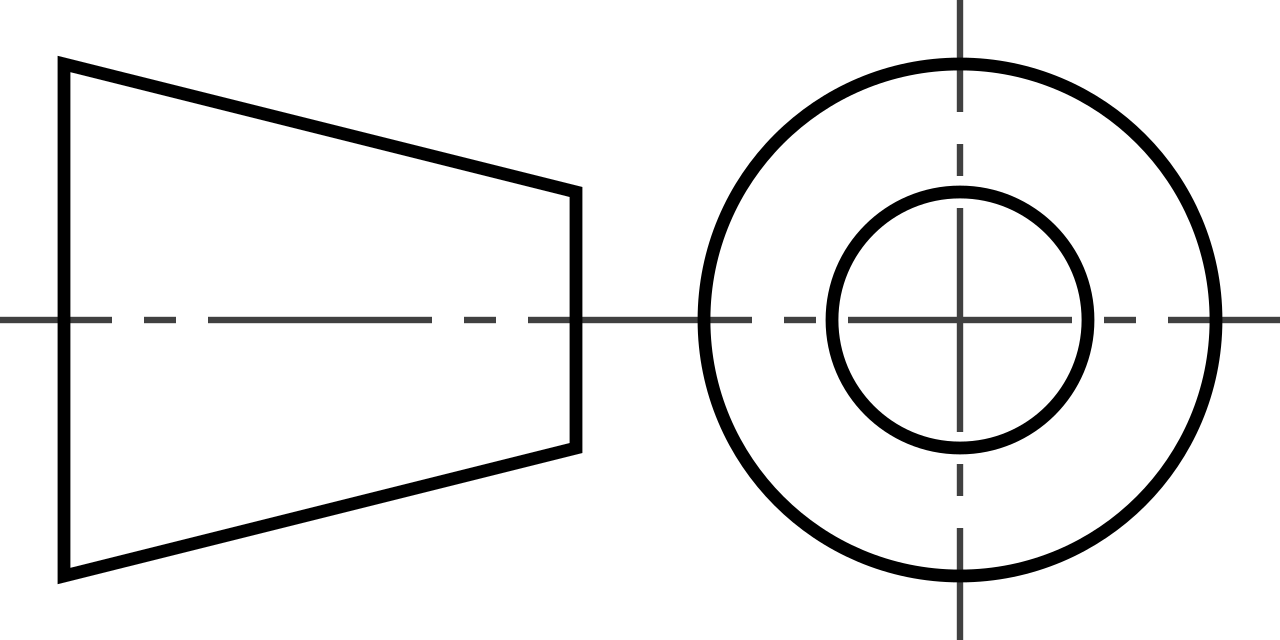
3rd Angle Projection - International conventions need to be used, such as, 3rd Angle projection, ISO, scale, units, etc which will be explained in criterion C.
Isometric Drawing / Projection An isometric drawing depicts the proposed solution in 3D, showing shape and form.
Exploded Isometric Drawing
- An isometric drawing of an object with more than one component that depicts how the parts of assemblies fit together.
- The drawing is exploded to show component parts of a product and/or the sequence of assembly.
- Isometric drawings are produced at the final solution stage and are used as working drawings in the realization stage
Perspective Drawing A set of formal drawing techniques that depicts an object as getting smaller and closer together the further away they are. The techniques are one-point perspective, two-point perspective, and three-point perspective.
Scale Drawings The need to scale drawings is when the object is either too large or too small to create. Scale depends on a basic understanding of ratios so that an appropriate scale/ratio is chosen. A scale drawing shoes a real object with accurate sizes except they have all been reduced or enlarged by a certain ratio

Sketching versus formal drawing techniques
Sketches Rough drawings of ideas used to convey or refine the idea
Formal drawing techniques A type of drawing technique that has fixed rules, the most widely used being isometric projection and perspective drawing
- Spontaneous representations of ideas on paper without the use of technical aids
- Designers use a range of freehand drawings in the early stages of developing ideas to explore shape and form (3D) and constructional details (2D)
- Divergent thinking is prominent at this stage
- Often use annotations to explain the thinking behind visual image
Formal drawing techniques A type of drawing technique that has fixed rules, the most widely used being isometric projection and perspective drawing
- Include: orthogonal, isometric, exploded isometric, sectional parts and assembly drawings which are done with great precision and usually with mechanical drawing aids or in CAD programs
- Designers use these drawings at the realization or development stage where the product is to be made. They are used to communicate to the manufacturer
- Convergent thinking is prominent at this stage
Part and assembly drawings
Assembly Drawing A diagram that shows how components fit together to make a whole –drawings are typically presented in an exploded view.
Component Drawing [Parts] Orthographic drawings of the components of an assembly containing details just about that component.
Parts Drawing Provides the information to assemble a product with the added benefit of having a list of parts [LOP] or a bill of materials [BOM]




No comments:
Post a Comment